Head: András Váradi, PhD, DSc, member of Academia Europaea
Pathological mineralisation develops in form of hydroxyapatite in organs and tissues where mineralisation is not supposed to happen. As cardiovascular diseases, the major cause of death in industrial societies, are strongly associated with calcification of arteries and other organs, there is a high demand for preventing this pathology.
The Laboratory is investigating the mechanism of mineralization/calcification and it is their aim to develop intervention/prevention therapies on preclinical level. In order to do so they develop novel animal models.
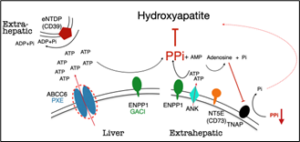
The molecular mechanism of regulation of ectopic calcification is illustrated on Figure 1.
Toward a prevention therapy using oral delivery of pyrophosphate:
Pyrophosphate (PPi) is a key endogenous metabolite controlling/preventing unwanted calcification. For decades it was the general opinion that due to its zero bioavailability its oral delivery is not feasible. The Váradi-group demonstrated that in spite of the general dogma a small amount of orally delivered PPi appears in the circulation and effectively reduces calcification* in the animal models of two model calcification diseases, pseupseudoxanthomadoxanthoma elasticum (PXE) and General Arterial Calcification in Infancy (GACI) [Dedinszki et al, 2017]. They also found the optimal salt from and formulation of PPi and showed that it is up-taken in healthy volunteers and in PXE-patients [Kozak et al, 2021].
Novel animal models:
The group created a novel animal model to study neurogenic heterotopic ossification and discovered that adrenaline modulates while PPi inhibits calcification [Tőkesi et al, 2020].
The group embarked upon to study diabetes mellitus (DM)-associated calcification. To perform such investigations was not possible earlier because of the lack of suitable animal models. They developed a DM-mouse model on Abcc6-/- genetic background which shows DM-induced calcification. This model allows them to delineate the sequence of molecular events results in calcification of the arteries, the eye, and the kidney. The model is proved to be suitable to test therapeutical approaches [Fülöp et al, manuscript in preparation].
Patents
Oral pyrophosphate for use in reducing tissue calcification, EP3512530A1, US16/333,856.
The patents are owned by RCNS (85%) and the Netherland Cancer Institute, NKI (15%). Upon the agreement between the two owners NKI licensed the patent to Panorama Research Inc (Palo Alto, CA, USA) in 2019; the license is being forwarded in 2024 to PXE International Inc (Damascus, MD, USA) for USA market and to PannonPharma (Hungary) for the European market.
Clinical trials
Trials using oral pyrophosphate are registered and started in PXE [NCT04868578, clinicaltrials.gov] and in systemic sclerosis [NCT04966416, clinicaltrials.gov].
Regular conference
The biannual International Meeting on Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum and other Calcification Diseases are organized by the Laboratory in Budapest since 2007.
- Piet Borst, The winner of the 2023 Lasker-Koshland Special Achievement Award in Medical Science (JAMA, Published online September 21, 2023): “It is PPi that prevents the unwanted calcification. This discovery led to several new attempts to treat patients with PXE. The cutest one was devised by my Budapest colleague Andras Varadi: oral PPi!”
Members
Head
András Váradi, PhD, DSc, member of Academia Europaea (https://m2.mtmt.hu/gui2/?type=authors&mode=browse&sel=authors10000030)
Postdocs
Viola Pomozi, PhD (https://m2.mtmt.hu/gui2/?type=authors&mode=browse&sel=authors10015262)
Krisztina Fülöp, PhD (https://m2.mtmt.hu/gui2/?type=authors&mode=browse&sel=authors10015259)
Eszter Kozák, PhD (https://m2.mtmt.hu/gui2/?type=authors&mode=browse&sel=authors10061918)
Assistants
Györgyi Vermes
Gabriella Szoták
Recent Publications
Dedinszki D*, Szeri F*, Kozák E, Pomozi V, Tőkési N, Mezei TR, Merczel K, Letavernier E, Tang E, Le Saux O, Arányi T, van de Wetering K, Váradi A. (2017) Oral administration of pyrophosphate inhibits connective tissue calcification. EMBO Mol Med. 9:1463-1470
Kozák E, Fülöp K, Tőkési N, Rao N, Li Q, Terry SF, Uitto J, Zhang X, Becker C, Váradi A*, Pomozi V*. (2022) Oral supplementation of inorganic pyrophosphate in pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Exp Dermatol. 31:548-555.
Pomozi V, Julian CB, Zoll J, Pham K, Kuo S, Tőkési N, Martin L, Váradi A, Le Saux O. (2019) Dietary Pyrophosphate Modulates Calcification in a Mouse Model of Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum: Implication for Treatment of Patients. J Invest Dermatol. 139:1082-1088.
Borst P, Váradi A, van de Wetering K. (2019) PXE, a Mysterious Inborn Error Clarified. Trends Biochem Sci. 44:125-140.
Tőkési N, Kozák E, Fülöp K, Dedinszki D, Hegedűs N, Király B, Szigeti K, Ajtay K, Jakus Z, Zaworski J, Letavernier E, Pomozi V, Váradi A. (2020) Pyrophosphate therapy prevents trauma-induced calcification in the mouse model of neurogenic heterotopic ossification. J Cell Mol Med. 24:11791-11799.
Kozák E*, Bartstra JW*, de Jong PA, Mali WPTM, Fülöp K, Tőkési N, Pomozi V, Risseeuw S, Norel JO, van Leeuwen R, Váradi A*, Spiering W*. (20230 Plasma Level of Pyrophosphate Is Low in Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum Owing to Mutations in the ABCC6 Gene, but It Does Not Correlate with ABCC6 Genotype. J Clin Med. 12:1047.
Kozák E, Szikora B, Iliás A, Jani PK, Hegyi Z, Matula Z, Dedinszki D, Tőkési N, Fülöp K, Pomozi V, Várady G, Bakos É, Tusnády GE, Kacskovics I, Váradi A. (2021) Creation of the first monoclonal antibody recognizing an extracellular epitope of hABCC6. FEBS Lett. 595:789-798.
Hsu VM, Kozák E, Li Q, Bocskai M, Schlesinger N, Rosenthal A, McClure ST, Kovács L, Bálint L, Szamosi S, Szücs G, Carns M, Aren K, Goldberg I, Váradi A*, Varga J*. (2022) Inorganic pyrophosphate is reduced in patients with systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 61:1158-1165.
*shared authorship
Collaborations
Queens’s University, Belfast (UK):
Physiology of calcification; state of art imaging
Panorama Research Inc (Palo Alto, CA, USA):
Development of novel pyrophosphate compounds
Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, University of Szeged, Szeged (Hungary):
Clinical trial in Systemic Sclerosis
Department of Vascular Medicine, University Medical Center Utrecht, Utrecht University (The Netherlands):
Pyrophosphate as a biomarker in calcification diseases
PannonPharma Inc (Hungary):
Development of GMP-quality pyrophosphate salts for clinical trials

